Application Programming Interface (API)
IMPORTANT
If you're planning to use the whitson external API, contact support@whitson.com for an onboarding session.
1. Basics
We can set up an API connection with associated authorization (OAuth) per request. Credentials, secrets and tokens are provided by our third-party authentication vendor. This will provide you with client specific API documentation, where the different endpoints are explained in detail. More API endpoints can be implemented on request. A complete list of available endpoints can be found here.
What is an endpoint?
An endpoint is like a specific destination or address that allows your software to interact with a particular functionality provided by the API. It's a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) where you can send requests to access or manipulate data. Each endpoint typically corresponds to a specific operation or resource, making it a defined entry point for communication with the API
The conventions for HTTP requests in whitson+ are following:
- POST: send data to whitson+
- GET: extract data from whitson+
- PUT: edit data for existing data object in whitson+
- PATCH: Partially update data objects in whitson+
- DELETE: delete data object in whitson+
IMPORTANT
- We kindly ask you to be mindful about requests of access tokens. Try to limit the token request to 1 per work session. Token is valid for 24 hours following request.
- Store
CLIENT_IDandCLIENT_SECRETin a secure place, as they grant access to alter your database via the endpoints.
Tips
- You may find it useful to set up environment variables while working with the API.
- Below is an example of setting up environment variables.
export CLIENT_NAME=<your company name> e.g. if you whitson<sup>+</sup> url is <company>.whitson.com, your CLIENT_NAME would be <company>
export CLIENT_ID=<authentication account id>
export CLIENT_SECRET=<authentication account secret>
export WHITSON_API_TOKEN=<bearer token for endpoints authentication>
2. Common HTTP Errors and Status Codes
- 400 Bad Request: The server cannot process the request due to malformed syntax or invalid data.
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication is required to access the resource, but the client has not provided valid credentials.
- 403 Forbidden: The server understood the request but refuses to authorize it, typically due to lack of permissions.
- 404 Not Found: The server cannot find the requested resource, often due to a broken or dead link.
- 405 Method Not Allowed: The request method (GET, POST, etc.) is not supported for the requested resource.
- 408 Request Timeout: The server terminated the connection because the client did not complete the request within the server's specified timeout period.
- 409 Conflict: This error indicates that the request could not be completed due to a conflict with the current state of the target resource. It usually occurs in situations where the client's request conflicts with the server's expectations or the current state of the resource, such as when attempting to update a resource that has been modified by another client.
- 422 Unprocessable Entity: This error typically occurs when the server understands the content type of the request entity but is unable to process the contained instructions. It's often used in the context of validation errors, indicating that the server cannot process the provided data due to semantic errors.
- 500 Internal Server Error: A generic error message indicating that something has gone wrong on the server's end.
- 502 Bad Gateway: The server acting as a gateway received an invalid response from an upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable: The server is temporarily unable to handle the request due to overloading or maintenance.
- 504 Gateway Timeout: The server acting as a gateway did not receive a timely response from an upstream server.
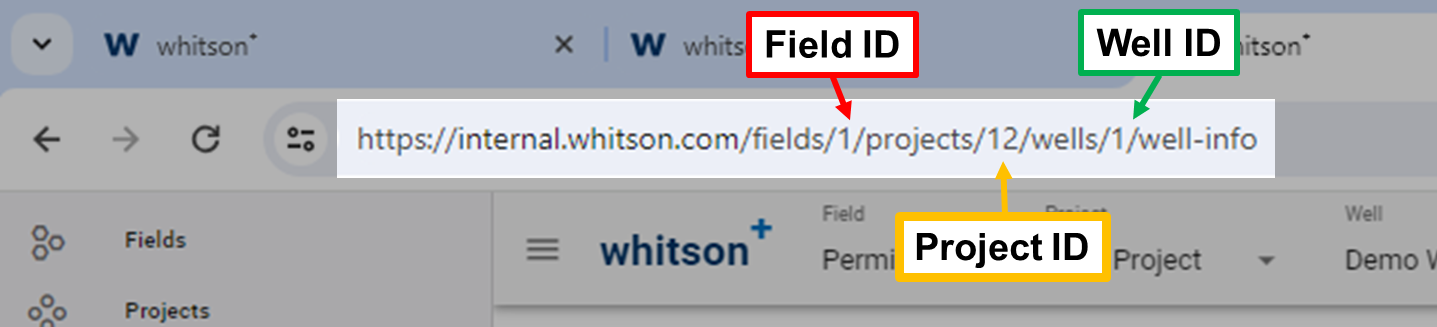
3. Software Heirarchy: Fields, Projects and Wells
whitson+ is organized into fields, projects, and wells, each of them tied to a numeric ID used to identify the well and it's location in the database. If you need the Field ID, Project ID or the Well ID for any of the API workflows, you can get them from the URL like so:
4. Some Helpful Tools
If you would like to use the whitson external API, we recommend using our API wrapper whitson_connect. This library provides a more convenient interface for interacting with the API, often abstracting away some of the lower-level details and making it easier to use.
To get started with whitson_connect, we recommend to
- Download Visual Studio Code here
- Download Python 3.12 here
- Download three common python librariesusing 'pip install'.
Run the following commands after installing python
- pip install requests
- pip install pandas
- pip install pydocs
requests is a simple yet powerful HTTP library for making requests to web servers. It allows you to send HTTP requests, such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc., and handle the responses easily. It's widely used for interacting with APIs, downloading web content, and web scraping.
pandas is popular data manipulation and analysis library that provides data structures like DataFrames and Series, making it easier to work with structured data. It's widely used for data cleaning, transformation, and analysis in data science and engineering. Install Command: pip install pandas
pyodbc is a library that provides a bridge between Python and ODBC-compliant databases, allowing you to connect to, query, and interact with databases like SQL Server, MySQL, and others from within Python scripts. Install Command: pip install pyodbc
Questions? Schedule a session with our support team by e-mailing support@whitson.com.